Organizational behavior (OB) is a field that examines how individuals, groups, and structures interact within a workplace setting. OB helps organizations improve productivity, foster collaboration, and create a positive work environment by delving into topics such as motivation, leadership, communication, and culture.
This blog explores the key aspects of organizational behavior, including the importance of organizational behavior, its foundational elements, and real-world applications. Additionally, we’ll dive deep into the theories and models that shape this field and discuss how OB principles can be applied to improve workplace dynamics. Whether you’re a student preparing for a content writer interview, a professional seeking to enhance your career, or simply curious about workplace psychology, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights.
What is Organizational Behavior?
Organizational behavior (OB) is the study of how individuals and groups interact within an organization. This discipline examines human behavior, leadership, team dynamics, communication, and decision-making processes in professional settings. Understanding organizational behavior enables businesses to create effective strategies that enhance productivity, employee satisfaction, and overall performance.
Importance of Organizational Behavior
Organizational behavior (OB) plays a vital role in the success of modern businesses by offering insights into human behavior within professional settings. It serves as a foundational pillar for creating effective, collaborative, and efficient workplaces. Here is a detailed exploration of the importance of organizational behavior:
1. Improves Employee Engagement and Satisfaction
One of the primary objectives of organizational behavior is to enhance employee engagement and satisfaction. By understanding employees’ needs, preferences, and motivations, organizations can create a supportive and rewarding work environment.
Example: Companies like Salesforce and Adobe actively foster a culture of feedback and recognition. Regularly appreciating employees’ contributions improves job satisfaction and reduces turnover rates.
2. Promotes Teamwork and Collaboration
OB delves into group dynamics and team-building strategies, ensuring harmonious collaboration among employees. It emphasizes the importance of shared goals, mutual respect, and effective communication Skills in achieving organizational objectives.
Example: Agile project management frameworks used in tech companies rely heavily on principles of organizational behavior to promote teamwork, adaptability, and accountability.
3. Enhances Leadership Effectiveness
Effective leadership is the cornerstone of organizational success. OB provides leaders with frameworks to understand team dynamics, decision-making processes, and conflict-resolution strategies. This equips them to inspire, guide, and support their teams toward achieving common goals.
Example: Transformational leadership, which emphasizes motivation and employee development, is grounded in organizational behavior principles. Leaders like Satya Nadella at Microsoft have used such approaches to revitalize company culture and drive innovation.
4. Increases Organizational Efficiency and Productivity
By optimizing workflows, communication channels, and employee roles, OB contributes to improved organizational efficiency. It encourages data-driven decision-making and the use of behavioral insights to streamline processes.

Example: Toyota’s implementation of the lean manufacturing system incorporates OB concepts to eliminate waste, improve quality, and enhance overall productivity.
5. Facilitates Change Management
In today’s dynamic business environment, organizations often transform, whether through mergers, technological advancements, or market expansions. OB plays a critical role in understanding and addressing employee resistance to change.
Example: When Starbucks introduced digital ordering through its mobile app, the company used OB strategies to train employees and align their mindset with the new workflow. This helped ensure a smooth transition and widespread acceptance of the change.
6. Supports Conflict Resolution
Conflicts are inevitable in any workplace, but their effective resolution is key to maintaining a healthy organizational culture. OB provides tools and strategies to identify sources of conflict, address grievances, and foster constructive dialogue.
Example: Organizational mediation sessions and grievance handling policies are informed by OB theories, ensuring fair and amicable conflict resolution.
7. Drives Innovation and Creativity
Organizations that understand and implement OB principles are more likely to foster innovation. OB encourages creating an environment where employees feel valued, leading to open communication and the generation of fresh ideas.
Example: Companies like 3M and Google allow employees to dedicate time to personal projects, fostering innovation and cultivating groundbreaking ideas like Post-it Notes and Gmail.
8. Strengthens Organizational Culture
A robust organizational culture aligns employees with the company’s vision, mission, and values. OB helps in identifying the cultural elements that drive performance, loyalty, and employee satisfaction.
Example: Zappos is renowned for its unique and customer-focused culture, built on principles of OB that emphasize employee happiness and empowerment.
9. Enables Better Decision-Making
OB enhances decision-making by incorporating insights into human behavior, motivations, and group dynamics. Leaders can make informed decisions that consider employee needs and organizational goals.
Example: Data-driven approaches to talent management, such as people analytics, are rooted in OB principles, helping organizations make evidence-based decisions about hiring, promotions, and training.
10. Ensures Ethical Practices and Corporate Social Responsibility
Organizational behavior emphasizes ethical decision-making and corporate social responsibility (CSR). It promotes transparency, fairness, and sustainability in organizational practices.
Example: Unilever’s commitment to sustainability and ethical business practices is a reflection of organizational behavior principles, aligning business goals with societal welfare.
Theories and Models of Organizational Behavior
Understanding organizational behavior involves exploring various theories and models that explain how individuals and groups act within organizations. Below is an in-depth look at some of the most prominent theories:
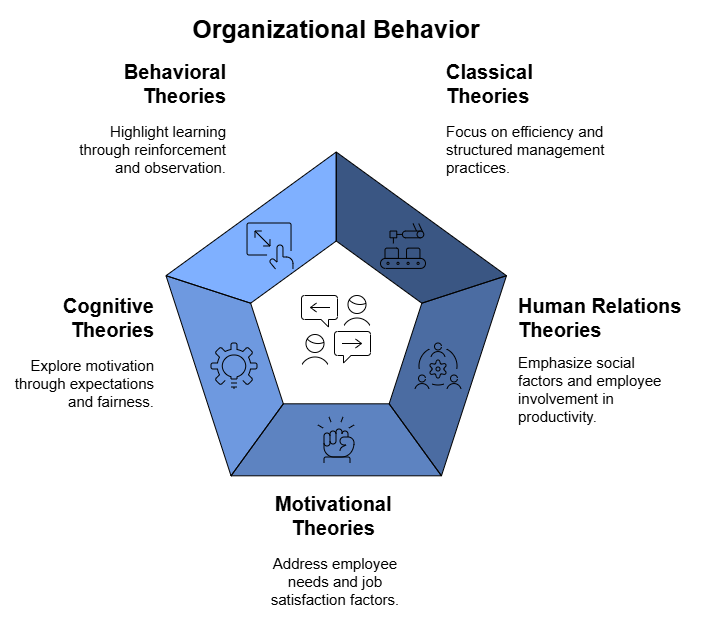
1. Classical Theories
-Scientific Management Theory
Developed by Frederick Taylor, this theory emphasizes efficiency and productivity. Taylor advocated breaking tasks into smaller units and standardizing workflows.
Real-world Example: Assembly lines in manufacturing industries often follow Taylor’s principles to enhance production efficiency.
-Administrative Management Theory
Proposed by Henri Fayol, this theory outlines management functions such as planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating, and controlling.
2. Human Relations Theories
-Hawthorne Studies
Conducted by Elton Mayo, these studies revealed that social factors and employee involvement significantly impact productivity.
Example: Modern-day team-building exercises and open office layouts encourage collaboration, a concept rooted in the Hawthorne studies.
3. Motivational Theories
-Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow identified five levels of needs: physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization. Employees perform best when these needs are fulfilled.
Example: Companies providing healthcare, career development opportunities, and recognition programs address Maslow’s needs.
-Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
This theory classifies workplace factors into motivators (e.g., achievements, recognition) and hygiene factors (e.g., salary, work conditions). Both are essential for job satisfaction.
4. Cognitive Theories
-Expectancy Theory
Proposed by Victor Vroom, this theory suggests that employees are motivated when they believe their efforts will lead to desired outcomes.
Example: Performance-based bonuses are designed on expectancy theory principles.
-Equity Theory
Developed by John Stacey Adams, this theory states that employees assess fairness by comparing their input-output ratio with others.
Example: Salary disparities within the same role can demotivate employees, aligning with equity theory.
5. Behavioral Theories
-Operant Conditioning
B.F. Skinner’s model emphasizes reinforcement and punishment to influence behavior.
Example: Rewarding employees for meeting targets with incentives aligns with operant conditioning.
-Social Learning Theory
Albert Bandura highlighted the role of observation and imitation in learning behaviors.
6. Contingency Theories
-Fiedler’s Contingency Model
This theory states that leadership effectiveness depends on the leader’s style and the situation.
-Path-Goal Theory
Proposed by Robert House, it emphasizes that leaders should adjust their style based on employee needs and work environments.
Characteristics of Organizational Behavior in the Workplace
Organizational behavior (OB) in the workplace involves studying and applying insights into how individuals and groups behave within an organizational environment. By analyzing and implementing OB principles, organizations can create environments that foster collaboration, improve employee satisfaction, and enhance overall productivity.
Here is a detailed look at how OB plays out in different aspects of the workplace:
1. Leadership and Management

Leadership plays a central role in organizational behaviour. Effective leaders understand the nuances of human behaviour, which enables them to guide their teams, make strategic decisions, and resolve conflicts.
Key Applications:
- Adopting different leadership styles (e.g., transformational or situational leadership) to suit team needs.
- Encouraging open communication to build trust and transparency.
- Using motivational theories like Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to inspire and engage employees.
Example: Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, has used empathetic leadership to transform the company’s culture, fostering innovation and collaboration among employees.
2. Employee Motivation and Productivity
Understanding what drives employees to perform their best is a core focus of OB. Motivation is not a one-size-fits-all concept; it varies based on individual preferences, workplace conditions, and career aspirations.
Key Applications:
- Implementing incentive programs and performance-based rewards.
- Offering professional growth opportunities through training and development.
- Using Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory to address both hygiene factors (e.g., salary, work environment) and motivators (e.g., recognition, meaningful work).
Example: Companies like HubSpot focus on employee empowerment by providing flexible work schedules and career development resources, resulting in higher productivity and job satisfaction.
3. Team Dynamics and Collaboration
Groups and teams are integral to workplace success. Organizational behavior helps organizations understand group dynamics, ensuring that teams operate effectively and achieve their goals.
Key Applications:
- Assigning roles and responsibilities that align with team members’ strengths.
- Promoting psychological safety, where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and feedback.
- Resolving interpersonal conflicts using collaborative conflict resolution techniques.
Example: The agile methodology, widely used in software development, leverages OB principles to enhance team collaboration and adaptability, ensuring successful project delivery.
4. Workplace Diversity and Inclusion
In today’s globalized world, diverse and inclusive workplaces are no longer optional—they are essential. Organizational behaviour helps businesses embrace diversity by understanding cultural differences and promoting equality.
Key Applications:
- Conducting diversity and sensitivity training to reduce unconscious biases.
- Implementing policies that support inclusivity, such as flexible work arrangements for employees with different needs.
- Encouraging cross-cultural collaboration to drive innovation and creativity.
Example: Companies like IBM have made diversity and inclusion central to their corporate strategy, ensuring equitable opportunities for employees of all backgrounds.
5. Conflict Resolution and Stress Management
Conflicts are inevitable in any organization, but how they are managed can make or break team dynamics. Organizational behaviour provides frameworks for identifying the root causes of conflicts and addressing them constructively.

Key Applications:
- Using the Thomas-Kilmann Conflict Mode Instrument (TKI) to determine the most effective approach to resolve disputes.
- Encouraging mediation to facilitate dialogue between conflicting parties.
- Implementing stress management programs, such as mindfulness training and employee assistance programs (EAPs).
Example: Organizations like Accenture offer holistic wellness programs to help employees manage workplace stress, leading to better overall performance.
6. Organizational Culture and Ethics
A strong organizational culture creates a shared sense of purpose among employees and aligns their goals with the company’s vision. Ethical practices further reinforce trust and loyalty among employees and stakeholders.
Key Applications:
- Establishing a clear mission and core values that resonate with employees.
- Rewarding ethical behavior and discouraging unethical practices through transparent policies.
- Fostering a culture centered on responsibility and ongoing growth.
Example: Patagonia, an outdoor clothing company, has built a culture centered on environmental sustainability and ethical practices, inspiring employee and customer loyalty alike.
7. Change Management
The modern workplace is constantly evolving due to technological advancements, market shifts, and organizational restructuring. Organizational behavior equips leaders with strategies to manage change effectively and reduce resistance among employees.

Key Applications:
- Conveying the reasons for change and its advantages to employees.
- Engaging employees in the change process to enhance support and minimize resistance.
- Providing training and support to help employees adapt to new processes or technologies.
Example: When Adobe transitioned to a subscription-based model for its software, the company used OB principles to align its workforce with the new business strategy, ensuring a smooth transformation.
8. Performance Management and Goal Setting
Performance management systems are designed to evaluate employee contributions and ensure alignment with organizational objectives. OB principles enhance the effectiveness of these systems by considering individual and team behaviors.
Key Applications:
- Establishing SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—helps maintain clarity and focus.
- Providing regular feedback and coaching to help employees achieve their full potential.
- Using performance appraisal systems that are fair and transparent.
Example: Deloitte revamped its performance management system to focus on real-time feedback and coaching, improving employee satisfaction and performance.
Conclusion
Organizational behavior (OB) is more than just a field of study—it’s a critical aspect of building successful and harmonious workplaces. By understanding how individuals, groups, and structures interact within an organization, businesses can unlock their full potential. OB principles guide leaders in creating positive work environments, fostering collaboration, and enhancing productivity, all while aligning with organizational goals.
Whether you’re a student, a professional, or a leader aiming to improve workplace dynamics, applying the insights of organizational behavior can drive growth, innovation, and satisfaction across every level of an organization. Embracing OB not only benefits businesses but also creates a workplace where employees thrive, paving the way for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- How does organizational behavior contribute to employee retention?
Organizational behavior helps identify factors like job satisfaction, work environment, and leadership quality that influence employee retention. By addressing these factors, organizations can reduce turnover. - What is the difference between organizational culture and organizational behavior?
Organizational culture refers to the shared values, beliefs, and practices within an organization, while organizational behavior focuses on understanding and managing individual and group dynamics within that culture. - How is technology shaping the field of organizational behavior?
Technology impacts organizational behavior by enabling remote work, improving communication, and providing tools like people analytics to make data-driven decisions about workplace dynamics. - What role does communication play in organizational behavior?
Effective communication is central to organizational behavior as it ensures clarity, reduces conflicts, and enhances collaboration, ultimately leading to a more productive workplace. - How can organizational behavior help in managing workplace diversity?
OB provides insights into cultural differences and promotes strategies like sensitivity training and inclusive policies to create a harmonious and equitable work environment.
