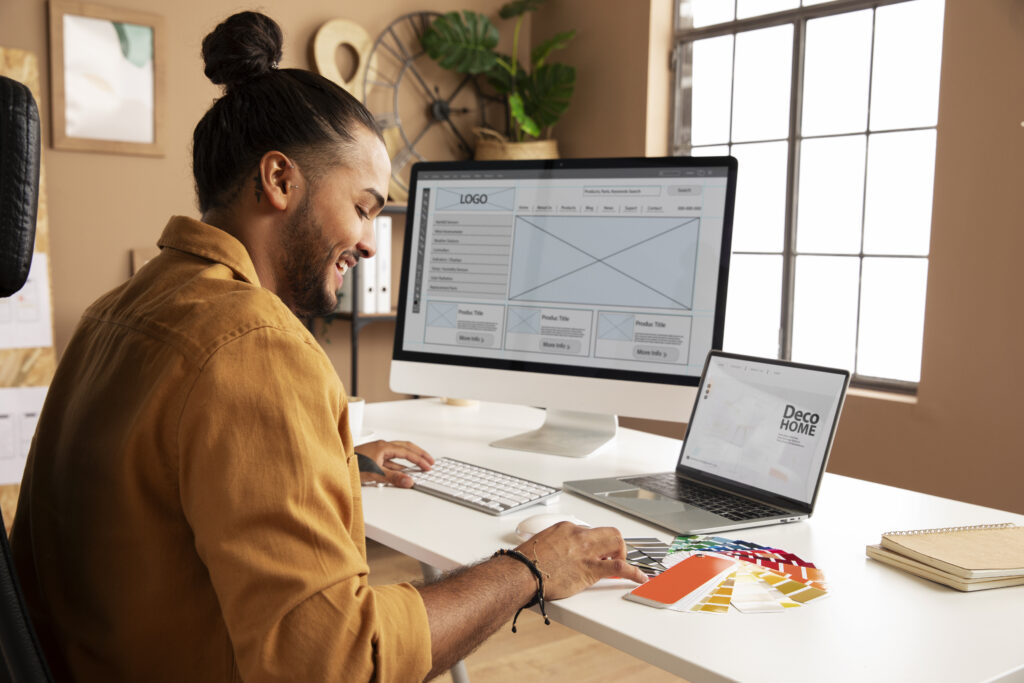
UI design, or User Interface design, focuses on creating visually appealing and intuitive interfaces for digital products. It encompasses visual design, interactive elements, and information architecture, aiming to enhance user experience. Effective UI design is simple, and consistent, and prioritizes usability, using visual hierarchy and user feedback for improvements. Real-world examples like Apple’s iOS and Google Search highlight the impact of good UI design. Best practices include understanding your users, designing for accessibility, adopting a mobile-first approach, optimizing performance, and iterating regularly. UI design is essential for creating digital products that delight users and drive business success.
What Is UI Design?
UI design, or User Interface design, is the process of designing the visual layout and interactive elements of a digital product. This includes everything users interact with on a screen, such as buttons, icons, spacing, typography, color schemes, and responsive design. The main goal of UI design is to enhance the user’s experience by making the interface intuitive, easy to use, and aesthetically pleasing.
Key Components of UI Design
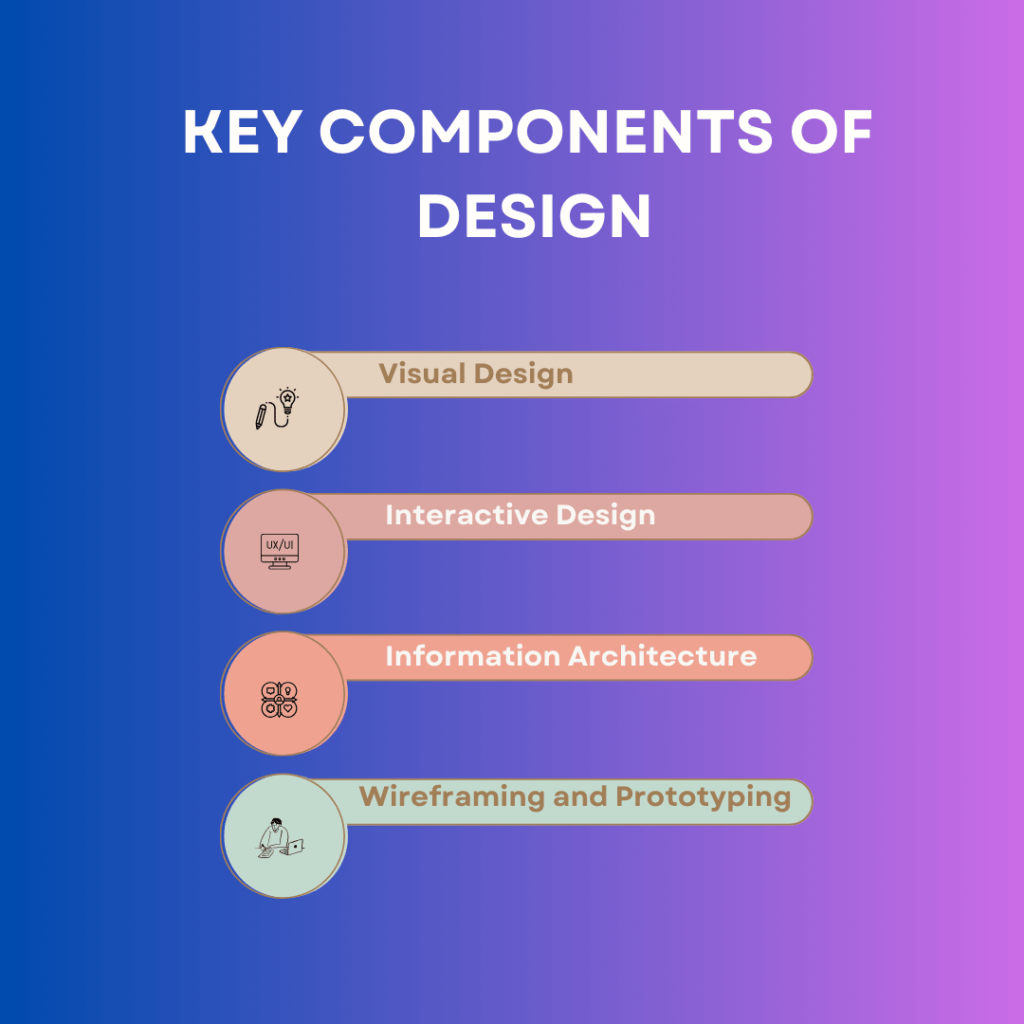
1. Visual Design
Visual design focuses on the aesthetics of the interface, ensuring that it is visually appealing and aligned with the brand’s identity. This includes elements such as:
- Color Schemes: Choosing colors that enhance readability and convey the right mood.
- Typography: Selecting fonts that are legible and match the overall design style.
- Images and Icons: Using relevant images and icons to aid navigation and understanding.
- Layout and Spacing: Organizing elements in a way that is visually pleasing and easy to follow.
2. Interactive Design
Interactive design deals with how users interact with the interface. This includes:
- Buttons and Controls: Designing buttons, sliders, and other controls that are easy to use.
- Navigation: Creating a clear and intuitive navigation structure.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Providing feedback through animations, sounds, or messages to indicate the result of user actions.
3. Information Architecture
Information architecture involves organizing and structuring content within the application or website to ensure that users can find what they need quickly and easily. This includes:
- Sitemaps: Creating a hierarchical structure of pages and content.
- Navigation Systems: Designing menus and links that guide users through the content.
- Labeling: Using clear and concise labels for menus and buttons.
4. Wireframing and Prototyping
Wireframing and prototyping are essential steps in the UI design process:
- Wireframes: Simple sketches or blueprints that outline the basic structure and layout of a page without detailed design elements.
- Prototypes: More detailed and interactive versions of wireframes that allow for user testing and feedback before final development.
Tips for Effective UI Design
Creating an effective UI design involves more than just making an interface look good; it’s about ensuring usability, consistency, and user satisfaction. Here are some essential tips for designing an effective UI:
1. Keep It Simple
Simplicity is crucial in UI design. Avoid clutter by focusing on essential elements and minimizing unnecessary features. A clean, simple design enhances usability and provides a more enjoyable user experience.
2. Ensure Consistency
Consistency in design helps users quickly learn how to navigate your interface. Use the same color schemes, typography, and button styles throughout your application or website. This reduces confusion and creates a cohesive look.
3. Prioritize Usability
Usability should be at the forefront of your design process. Make sure that all interactive elements are easy to find and use. Conduct usability testing to identify and fix any issues that may hinder the user experience.
4. Use Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy helps guide users’ attention to the most important elements on the page. Use size, color, and placement to create a hierarchy that directs users to key features and information, making it easier for them to understand and navigate your interface.
5. Incorporate Feedback Mechanisms
Provide feedback through messages, animations, or other indicators to help users understand how to interact with the interface and recover from mistakes. Feedback gives users a sense of control and confidence in using your product.
Real-World Example: Google Search
Google Search is a perfect example of simplicity and usability in UI design. The search bar is prominently placed in the center of the page, making it easy for users to find and use. The interface is clean, with minimal distractions, allowing users to focus on their search queries.
Best Practices for UI Design
- Understand Your Users: Conduct user research to understand your target audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviors. This will help you design an interface that meets their expectations and enhances their experience.
- Design for Accessibility: Ensure that your interface is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. Use accessible color combinations, provide text alternatives for images, and ensure that all interactive elements are keyboard-navigable.
- Mobile-First Design: With the increasing use of mobile devices, it’s essential to design with a mobile-first approach. Ensure that your interface is responsive and provides a seamless experience across all devices.
- Focus on Performance: A slow interface can frustrate users and drive them away. Optimize your design for performance by minimizing large images, using efficient code, and reducing load times.
- Iterate and Improve: UI design is an ongoing process. Continuously gather feedback, conduct usability tests, and make improvements to your design. Regular updates and iterations will help you maintain a high-quality user experience.
Conclusion
UI design plays a crucial role in the success of digital products. By understanding the key components of UI design, following essential tips, and adhering to best practices, you can create interfaces that are not only visually appealing but also user-friendly and efficient. Remember to keep your design simple, consistent, and focused on usability. Conduct regular user research and testing to ensure that your design meets the needs of your target audience. By doing so, you’ll create a digital product that delights users and drives business success.
For those looking to break into the field or advance their careers in UI and UX design, Prepmagic is an excellent resource. As a leading platform for UI/UX interview preparation and career guidance, Prepmagic offers comprehensive resources, expert advice, and personalized coaching to help you ace your interviews and build a successful career in design. Whether you’re just starting or looking to refine your skills, Prepmagic is your go-to source for all things related to UI/UX design and interview preparation.
